[머신러닝] Chap 4 - Decision tree
머신러닝의 결정 트리 알고리즘은 데이터를 분할하기 위해 정보 엔트로피, 이득 비율, 지니 지수를 사용하며, 과적합 문제를 해결하기 위해 전후 가지치기를 적용합니다. 연속 값과 결측값 처리 방법도 설명되며, 다변량 결정 트리의 가능성에 대해서도 논의됩니다.
[머신러닝] Chap 4 - Decision tree
Disclaimer
📣 본 포스트는 조우쯔화의 단단한 머신러닝 책을 요약 정리한 글입니다.
Chap 4. Decision tree
4.1 Basic process
- Decision Tree Learning algorithm
- Input : Testing set $D$, Feature set $A$
Process :
- generate node $i$
- if $\forall D \in C$ :
- Mark node $i$ as a class $C$ leaf node, return
- if $A=\varnothing \ \text{or} \ \forall D $ take some value on $A$ :
- Mark node $i$ as a leaf node, label = majority class in $D$, return
- Set optimal splitting feature $a^*$ from $A$ (Entropy, GINI, etc…)
- for each value $a_{}^{v}$ in $a_{}$, do :
- Generate branch for node $i$ ; $D_v$ is subset of samples taking $a_{}^{v} \text{on } a_{}$
- if $D_v$ is empty :
- Mark $D_v$ as leaf node, label it with majority class in $D$, return
- else :
- $D_v$ = self($D_v$, $A \ \backslash \ {a_*}$)
Output : Decision tree with root node $i$
4.2 Split selection
Split by information entropy
- Information Entropy (or simply entropy)
- $f$ : Number of features
- Entropy 의미 : 클 수록 잘 분배되어 있는 것. 0에 가까울 수록 한쪽으로 편향되어 있다는 뜻 (작을 수록 순도가 높음)
- Gain of splitting samples by feature
- 모든 남아있는 feature에 대한 information gain을 계산하여 가장 gain이 높은 (엔트로피를 효과적으로 줄일 수 있는) feature를 택하여 분할을 진행
Split by gain ratio
- Gain ratio : Gain 자체가 커지게 하려면 attribute의 수가 많은 feature가 유리하게 작동함. 즉 이에 대한 보정을 하는 것이 gain ratio 보정(?)
- Gain ratio is biased towards features with fewer possible values : possible values 수가 많은 경우 (like case of ID) 저평가함.
Split by GINI Index
- Gini(D) : 임의의 2개 sample이 서로 다른 클래스일 확률. (Gini(D)가 클 수록 D의 purity는 높음)
- Gini index가 가장 작은 feature를 고름
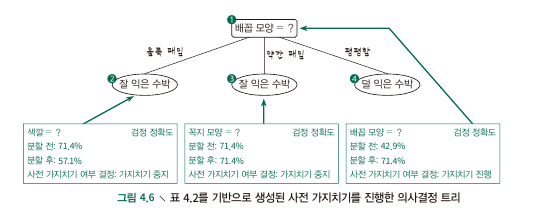
4.3 Pruning
- Deal with overfitting.
- General strategies : pre/post-pruning
- First, using hold-out method, split dataset into training and validation set
Pre-pruning
- comparing before/after splitting
- 가지치기를 하기 전에 splitting 과정에서부터 pre-pruning을 진행하는 것.
- validation set에 대한 accruacy를 splitting 전후로 계산, 그 rate가 늘어나지 않으면 prune, 그렇지 않으면 split
- Advantages : Reduce the risk of overfitting, computational cost of training and testing
- Disadvantages : Risk of underfitting
Post-pruning
- 이미 만들어진 decision tree에 대한 ‘post’ pruning
- 먼저 total tree에 대한 accruacy를 계산.
- 하위 node부터, pruning 전후의 accuracy 차이를 계산, 효용이 있다면 pruning 진행. (같다면 진행 x)
- Advantages : less prone to underfitting -> better generalization ability
- Disadvantages : training time of post-pruning is much longer (하위노드부터 하나씩 전부 따져봐야 하므로)
4.4 Continuous values & missing values
Continuous values
- Discetization Stretagy (Bi-partition) : Dataset D에서 feature a에 대해 t를 기준으로 2개의 group으로 나눔.
- 이 때 Split point의 후보 분할점이 되는 점
- Midpoint $T_a$가 사용되며, 이를 이용해 구한 Gain은 다음과 같음.
- a라는 property를 이용해 D를 분리할 때 t라는 새로운 변수까지 고려해서 gain이 최대화되는 t를 선택하겠다는 뜻.
Missing Values
- To solve problems :
- feature의 선택
- feature가 선택된 경우 샘플이 결측값이라면 어떻게 분할할 것인가.
- 특정 feature $a$에 대하여:
- $w_x$ : weight for sample $x$
- $D$ : total data
- $\tilde D$ : data that has values of $a$
- $\tilde D_k$ : $k$th sample(classifier’s ground truth)
- $\rho$ : 전체 Data 중 $a$의 데이터가 존재하는 비율 (weighted)
- $\tilde p_k$ : 결측값 없는 데이터 중 label : $k$의 비율 (weighted)
- $\tilde r_v$ : 결측값 없는 데이터 중 feature $a$에 대해서 $v$의 값을 갖는 비율 (weighted)
- Gain, Entropy의 재정의
- 만약 feature $a$로 분할 했는데 특정 sample $x$의 feature $a$가 결측값이라면, $x$를 모든 하위 node에 동일하게 귀속시키는 대신 그 가중치(weight)을 $w_x$에서 $\tilde r_v w_x$로 update한다.
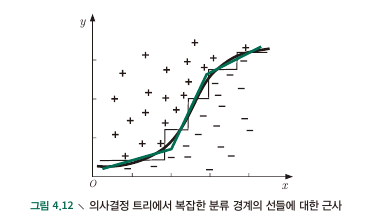
4.5 Multivariate Decision Trees
- Feature axis에 data point를 plot 하였을 때 Decision tree가 하는 일은 axis에 parallel한 경계선을 긋는 행위.
- Parallel하지 않은 대각선 line을 그릴 수 있다면?
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.