[제어공학개론] Lec 18 - Discrete time domain system
제어공학 개론의 18번째 강의에서는 이산 시간 영역 시스템에 대해 다루며, 물리적 세계와 사이버 세계의 연결, 샘플링 시간, 상태 공간 표현, 그리고 이산 시스템의 안정성 조건을 설명합니다. 이산 신호는 입력과 출력으로 구성되며, 안정성을 위해서는 시스템의 고유값이 단위 원 내부에 있어야 합니다.
📢Precaution
본 게시글은 서울대학교 심형보 교수님의 23-2 제어공학개론 수업 내용을 바탕으로 작성되었습니다.
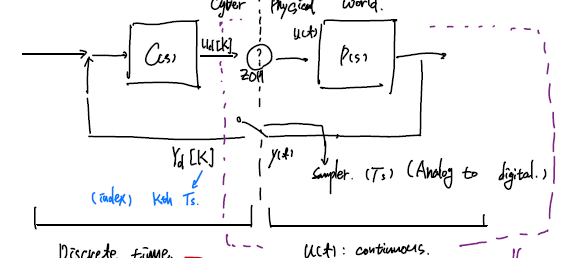
Discrete - Time domain system
Physical world는 analog이지만, Cyber world는 컴퓨터로 진행되므로, 일정한 시간 간격마다 system clock에 따라 sampling되고 결과가 출력됨.
Cyber world와 Physical world를 이어주는 2개의 선에서, Controller output 을 $P(s)$에 전달해주는 Actuator, 혹은 Digital to Analog Convert(DAC). 그리고 $P(s)$의 출력 $y$를 Sampler (Analog to Digtal Converter) (Switch형태로 표시) 가 있음.
Sampling time $T_s$에 대해서 Discrete signal을 $y_d[K]$의 형태로 index로 적음.
Discrete signal에는 $ y, t $ 2개에 대해 discrete할 수 있는데, 일단 여기서는 $t$가 discrete한 경우만 다룸.
그렇다면 Physical system 또한 $z$-transform에 의해 일종의 input-output이 있는 system으로 볼 수 있음.
$u_d[K]$가 input, $P_d[Z]$의 transfer function을 가지고, $y_d[K]$가 출력.
ZOH (Zero-order holder) :
Converter :
\[u(t) = u_d[K] \text{ for }KT_s\leq t \leq (K+1)T_s\]State-space representation of discrete system
Differential이 아닌 Difference(차분) equation이라고 불림
\[\begin{aligned}\bar{x}[K+1] &= \bar{A} \bar{x}[K] + \bar{B} \bar{u}[K] + W[K] \\\bar{y}[K] &= \bar{C} \bar{x}[K] + \bar{D} \bar{u}[K]\end{aligned}\]일종의 MDP(Markov decision process)
stochastic하게 만들기 위해 $W[K]$ 라는 랜덤확률변수를 도입하기도 함. (ML에서)
물리적 실체인 원래의 A, B, C, D 시스템으로부터 Sampling한 것이라고 볼 수 있음. (물론 컴퓨터에서 만들어진 system일 경우 애초에 실체가 discrete일수도)
recall the Variation of Constant Formula
\[\begin{aligned}x(t) &= x(0) e^{At} + \int_0^t e^{A(t-\tau)} B u(\tau) \, d\tau \\\bar{x}[1] &= x(T_s) = e^{A T_s} x[0] + \int_0^{T_s} e^{A(T_s - s)} B u(s) \, ds\end{aligned}\]when using ZOH, $u(s)$ is constant for one period.
\[\begin{aligned}\bar{x}[1] &= e^{A T_s} x[0] + \int_0^{T_s} e^{A(T_s - s)} \, ds \, \bar{u}[0] \\\bar{A} &= e^{A T_s}, \quad \bar{B} = \int_0^{T_s} e^{A(T_s - s)} \, ds \\\bar{C} &= C, \quad \bar{D} = D\end{aligned}\](단순히 sampling하는 것은 값을 바꾸지 않으므로.)
Stability of Discrete system
Continuous에서는 pole의 eigenvalue들이 좌반평면에 위치하는 Hurwitz 조건이 안정도에 대한 조건이었음.
Discrete에서는 $\bar A=e^{AT_s}$에서, $x[K] = \bar A^k x[0]$이므로, 이가 안정하기 위해서는 $\bar A$의 eigenvalue들이 모두 Unit circle 내부에 존재해야만 함.
일반적인 continous time domain에서는 그냥 simularity transform 만을 통해서 계산되므로, 단순히 eigenvalue들이 좌반평면에 있으면 되지만, discrete time에서는 transform을 거친 후 이를 k번 곱했을 때 $\lim\limits_{k\rightarrow \infty} \bar A^k$ 값이 수렴해야 하므로, 모든 eigenvalue들이 unit circle 안에 존재해야 값이 커지지 않음.
\[\begin{aligned}\bar{x}[K] &= \bar{A}^K \bar{x}[0] \\A^K &= (T J T^{-1})^K = T J^K T^{-1}\end{aligned}\]