[일반화학] Lec 07 - Physical Equilibrium
[일반화학] Lec 07 - Physical Equilibrium
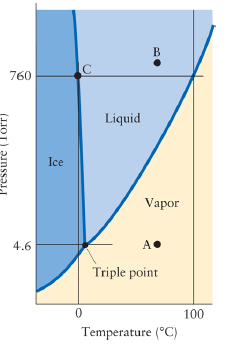
phase diagram
- T, P axis 위에서
특정 P에서의 Gibbs free energy
\[G(P) = G^0 + RTln({P\over P_0})\]- Solid, V(p)=const, G naught + V(pf-pi)로 표현
Clapeyron equation
- $dG = −SdT + VdP$ 로부터, alpha, beta라는 서로 다른 상의 경계에서의 식은
증기압 (vapor pressure)
\[\Delta G_{vap} = G_{gas}-G_{liq} = G_{gas}^0 +RTln({P\over P_0})-G_{liq}^0\]- at equibrilium, ΔG = 0
- naught : 1atm이므로 T1, P1 → T2, P2로 바뀔 때
- Vaporization : Molecular structure, Temperature에는 영향 받으나 Amount에는 Independent
Volatility and Intermolecular Forces
- High Vap pressure : low intermolecular forces
- e.g. 에탄올(O-H 수소결합) vs 디에틸 에테르 → 에탄올이 증기압 낮음. (결합 강함)
물에서의 solid-liquid boundary, negative slope
- by Clapeyron equation, ΔV < 0이므로 기울기가 아주 살짝 음으로 감
Solubility
- polar-polar끼리, nonpolar-nonpolar끼리 잘 녹음. → 중요한 Factor : Hydrogen Bonding
- polar - nonpolar 결합에서, nonpolar는 결합하는게 좋음 (induced dipole에 의해 결합 좋음) but, polar-polar 결합 끊고 polar-nonpolar결합 하는 것이 polar 입장에서 좋지 않음.
- nonpolar-nonpolar : 엔트로피증가에 의한 효과.
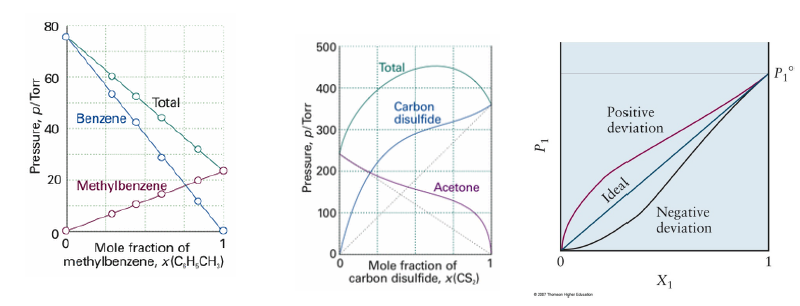
Raults Law for volatile A and B
- 돌턴의 분압법칙에 의해,
Henry’s Law of Solute
- B의 농도가 매우 낮다면, 몰분율에는 still proportional, but pure vapor pressure가 아닌 henry const에 비례함.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.