[신호처리] Lec 01 - Signal
신호처리에 관한 강의에서는 신호의 정의, 주파수, 푸리에 변환, 이미지의 푸리에 변환 및 K-공간 데이터에 대해 설명합니다. 신호는 독립 변수의 함수로 정의되며, 푸리에 변환을 통해 신호를 주파수 도메인으로 변환할 수 있습니다. 또한, 연속 신호의 샘플링과 양자화 과정을 통해 이산 신호가 생성되며, 디랙 델타 함수의 성질도 다루어집니다.
Precaution
본 게시글은 서울대학교 이종호 B 교수님의 SNU FastMRI Challange, 2021 Signal Processing을 바탕으로 제작되었습니다.
Definition, Preliminaries
- Signal
- 독립 변수의 함수
examples of signal :
- 1D signal : $y=f(t)$
2D signal : $f(x, y)=k$
$(x,y)$ can be position
$k$ can be brightness of the pixel
- 일반적인 이미지(eg. 점묘화) : ( $W\times H \times 3$ Matrix. RGB 각각의 밝기)
- Frequency
- 1초간 진동 횟수
- Fourier Transform
- Convert signal to frequency domain(spectrum)
Fourier Transform of an image
if Fourier transform applied to image, we get K-space data.
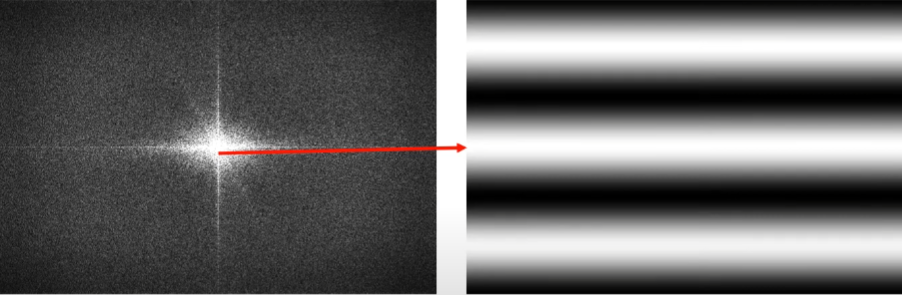
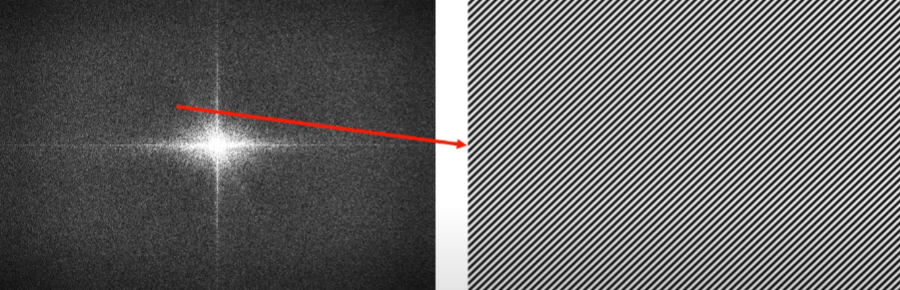
kspace data of the image
읽는 법은 잘 생각해보면 어렵지 않음. 가운데 지점은 constant이고, arbitary point를 잡았을 때 center를 시점으로 하는 vector의 방향으로 vector의 크기만큼의 Frequency를 가진 점의 밝기 만큼의 amplitude(밝기)의 wave임.
이런식으로 모든 점에 대응되는 wave를 겹치게 되면 grayscale의 원본 이미지를 얻을 수 있음.
distance from the center is proportional to frequency, while direction decides the angle
- spatially varying…
- Sampling, Alising
- CT, DT, Digital
Continuous time signal을 Sampling, Indexing 한 것이 Discrete time domain signal. 이후 quantization(결과값 혹은 함수값의 discrete화)한 것이 Digital signal.
- Indexing : integer index에서만 값이 존재.
Frequently used signals
- Complex exponential :
- Rotation : increasing t에 따라 반시계 방향으로 회전. Re, Im 축으로 proj 했을 때는 cos/sin의 sinusodial wave
Dirac’s Delta :
Continuous domain에서는 2가지 property를 만족해야 함.
- Definition
- Area
- Discrete Time domain 에서의 dirac’s delta는 더 쉽게 정의됨. 0일 때 1, 나머지일 때 0
Most important property of Dirac’s delta function
for arbitary $x(t)$,