[전선대 Assignment] K-means clustering, KNN classification
[전선대 Assignment] K-means clustering, KNN classification
Problem 1 - K means clustering
In this problem you will be asked to fill in the blanks to implement K means clustering algorithm via python.
Please read the comments carefully and fill in the TODO marks
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Import necessary libraries - Do not import more
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import plotly.express as px
import random
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Next import data and change to shapes we can easily use
df = px.data.iris()
X_s = []
for idx in range(len(df)):
X_element = [
df['sepal_length'][idx],
df['sepal_width'][idx],
df['petal_width'][idx]
]
X_s.append(X_element)
X_s = np.array(X_s)
# X_s is now an array of dimension(N, D), where N is the number of datapoints and D is the number of features for each datapoint
# For this problem each datapoint consists of 3 variables: sepal length, sepal width, and petal width
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
# This python class will be the main target of the problem. Fill in the blanks to correctly implement Kmeans algorithm.
class KMeansClustering:
def __init__(self, X, K):
""" Init function. We will save the input parmeters and initialize centroids
[Args]:
X : N x D np.ndarray of N datapoints each with D features
K : The number of clusters to consider
"""
self.K = K
self.X = X
self.N, self.D = X.shape
############################### TODO ################################### // Done?
self.cluster = np.zeros(self.N).astype(np.uint8)
self.centroid = np.zeros((self.K,self.D))
# creating centroid array of [k,d] dimension.
for key in range(self.K) : ## for K clusters, assign a random datapoint to each cluster
self.centroid[key] = self.X[random.randrange(self.N)]
def assign_cluster(self):
"""This function assigns each datapoint to the nearest cluster.
The distance metric is L2 distance
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
for item in range(self.N) :
dist = np.zeros(self.K)
for key in range(self.K): # calculate L2 dist
for feature in range(self.D):
dist[key]+=(self.X[item]-self.centroid[key])[feature] ** 2
# dist[j] = ||x_i - z_j||^2
self.cluster[item] = np.argmin(dist) #assigns cluster for min distance
def update_centroid(self):
"""This function updates centroids according to current assignment of clusters.
For each cluster, calculate the mean of each cluster and update its centroid.
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
for key in range(self.K) :
sortedarray = np.where(self.cluster==key)
# sorted array is a [1,1] tuple which contains [1,] np.ndarray
l = sortedarray[0].size
totalsum = np.zeros(self.D)
# for sum of each features
for i in sortedarray[0]: # for a single datapoint in kth cluster
for j in range(self.D): # add up values in totalsum for each feature
totalsum[j] +=self.X[i,j]
self.centroid[key] = totalsum/l
def calculate_distance(self):
"""This function calcuates the average distance from each datapoint to its assigned cluster.
Return the distance.
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
dist =0
for item in range(self.N) :
square=0
for feature in range(self.D) :
square+= (self.X[item]-self.centroid[self.cluster[item]])[feature] ** 2 # same method in assign_cluster
dist+=square**(1/2)
dist /= self.N #dist is a mean value
return dist
def run(self, steps=100):
"""This function runs K means clustering for given number of iterations.
For each iteration, you should assign clusters, update centroids and
report the final distance metric from each datapoint to its respective centroids.
Return the calculated distance
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
iter = 0
self.assign_cluster()
prev_dist = self.calculate_distance() #for inital distance
for iter in range(steps+1):
self.assign_cluster()
self.update_centroid()
if self.calculate_distance()==prev_dist: # if prev_dist == current_dist, stop iteration
break
else :
prev_dist = self.calculate_distance() # update prev_dist
print("Run ended with " + str(iter) + " iterations!")
return prev_dist
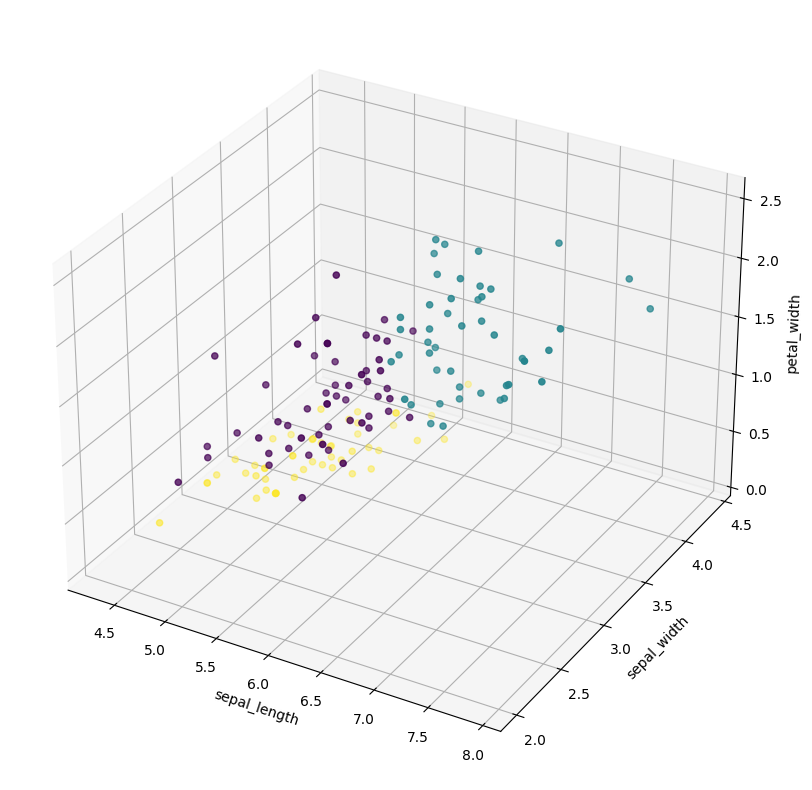
def visualize(self):
"""This fuction visualizes the current clusters"""
color_list = np.random.rand(self.K)
colors = []
for _idx in range(len(self.X)):
colors.append(color_list[self.cluster[_idx]])
colors = np.array(colors)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.scatter(X_s[:, 0], X_s[:, 1], X_s[:, 2], c=colors)
ax.set_xlabel('sepal_length')
ax.set_ylabel('sepal_width')
ax.set_zlabel('petal_width')
plt.show()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Initialize Kmeans model and start clustering!
# You may change K and steps if you want!
K = 3
Kmeans = KMeansClustering(X_s, K)
# run the Kmeans clustering algorithm for 10 steps
dist = Kmeans.run(steps=10)
print("For K : {} the distance was {}".format(K, dist))
Kmeans.visualize()
Output : Run ended with 6 iterations! For K : 3 the distance was 0.5138938958006479
Problem 2 - KNN classification
In this problem you will be asked to fill in the blanks to classify a new datapoint via KNN algorithm.
Please read the comments carefully and fill in the TODO marks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Again, import data and change to a form we can easily use
train_X = []
test_X = []
train_Y = []
test_Y = []
for idx in range(len(df)):
X_element = [
df['sepal_length'][idx],
df['sepal_width'][idx],
df['petal_width'][idx]
]
Y_element = [
df['species_id'][idx]
]
if idx % 5 != 0:
train_X.append(X_element)
train_Y.append(Y_element)
else:
test_X.append(X_element)
test_Y.append(Y_element)
X_train = np.array(train_X)
X_test = np.array(test_X)
y_train = np.array(train_Y)
y_test = np.array(test_Y)
# With this, train_X is an N x D array with N datapoints each with D features(sepal length, sepal width, petal width)
# train_y contains the groundtruth labels(species id) for each train_X datapoint
# In the rest of this question you will be asked to predict the species id for unknown datapoints
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
# This python class contains all necessary functions for a KNN classifier.
class KNN:
""" k-nearest neighbor classifier class """
def train(self, X, y):
""" Train the classifier using the given training data (X, y).
[Args]:
X: A numpy array of shape (N, D), where N is the number of data points, D is the dimensionality of each data point.
y: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing the training labels.
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
self.X_train = X
self.y_train = y
# setting property of class KNN
def inference(self, X_test, k=1):
""" For each test example in X, this method predicts its label by majority vote
from the k nearest training samples. It returns the predicted labels.
[Args]:
X: A numpy array of shape (N, D), where N is the number of data points, D is the dimensionality of each data point.
k: The number of neighbors to participate in voting.
[Returns]:
y_pred: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing predicted labels for the test data X,
where y_pred[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
# Compute the distance matrix below with the given metric.
dists = self.compute_distance(X_test)
# Predict the labels with the distance matrix.
y_pred = self.predict_labels(X_test, dists, k)
return y_pred
def euclidean(self, x1, x2):
"""Calculate and return euclidean distance between x1 and x2
[Args]
x1: Datapoint 1
x2: Datapoint 2
[Returns]
dist: Euclidean distance between input
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
D = x1.size # assume that x1.size = x2.size
dist = 0
for i in range(D):
dist+=(x1[i]-x2[i])**2
return dist**(1/2)
def compute_distance(self, X_test):
"""Computes the distance between the training data and test data,
[Args]:
X_test: A numpy array of shape (N, D), where N is the number of test data points, D is the dimensionality of each data point.
X_train: A numpy array of shape (M, D), where M is the number of training data points, D is the dimensionality of each data point.
[Returns]:
dists: A numpy array of shape (N, M) containing the distances
"""
N = X_test.shape[0]
M = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((N, M))
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
dists[i, j] = self.euclidean(X_test[i].squeeze(), self.X_train[j].squeeze())
return dists
def predict_labels(self, X_test, dists, k):
"""For the given test image, this method takes a majority vote from k closest points
to predict the class of the test image.
[Args]:
X_test: A numpy array of shape (N, D), where N is the number of test data points, D is the dimensionality of each data point.
dists: A numpy array of shape (N, M) containing distances between
k: The number of neighbors to participate in voting.
[Returns]:
y_pred: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing predicted labels for the test data
"""
############################### TODO ###################################
y_pred = np.zeros(len(X_test)) # len(X_test) = N
for i in range(len(X_test)):
idxsmallest = np.argpartition(dists[i], k)
# np.argpartition(ndarray ar, int i) : return array of range(1,k) th smallest index
candidate = np.zeros(len(X_test[0])+1)
# each element of array counts number of labels within kth nearest datapoint
for j in range(k) :
candidate[y_train[idxsmallest[j]]]+=1
# search nearest k datapoints and count the number of labels
maxval = np.max(candidate)
if np.where(candidate==maxval)[0].size>1 :
# when the count of each label is same, e.g) [10,10,0,0]
# in this case, use the prediction of k-1's value.
# even if k-1's result is same, it iterates until it gets single decision.
y_pred[i]=self.predict_labels(X_test, dists, k-1)[i]
else :
y_pred[i]=np.argmax(candidate)
# return the max value of candidate
return y_pred
def evaluate(self, y_pred, y):
"""
Compares the predicted labels to the ground truth y, and prints the classification accuracy.
[Args]:
y_pred: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing predicted labels
y: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing the groundtruth labels
[Returns]:
accuracy
"""
y_pred = np.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=1)
num_correct = np.sum(y_pred == y)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / y.shape[0]
return accuracy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# Now let's start classifying!
model = KNN()
model.train(X_train, y_train)
# Model used to test the performance.
K = 15
y_pred = model.inference(X_test, k=K)
acc = model.evaluate(y_pred, y_test)
# print("Accuarcy:", acc)
# Modify the number of k's and metrics to try as you want
num_ks = 50 # number of k's
metrics = ['l2']
# Run experiments
print_k_interval = 5
result = dict(zip(metrics, [[] for _ in range(len(metrics))]))
for metric in metrics:
print("running KNN with {} distance metric".format(metric))
for k in range(1, num_ks+1):
if k % print_k_interval==0:
print(" processing... k={:3d}".format(k))
y_pred = model.inference(X_test, k=k)
acc = model.evaluate(y_pred, y_test)
result[metric].append(acc)
print()
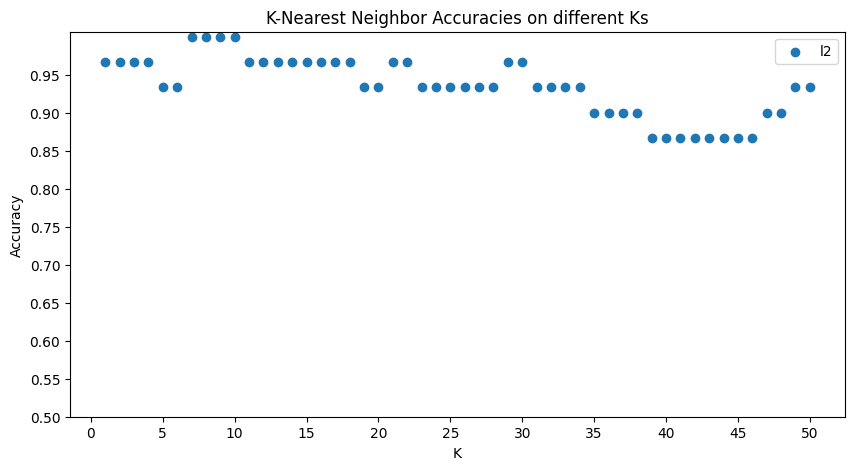
# Visualize and report the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
x_axis = np.arange(1, num_ks+1, 1)
for i, metric in enumerate(metrics):
ax.scatter(x_axis, result[metric], label = metric)
ax.set(title="K-Nearest Neighbor Accuracies on different Ks")
ax.set(xlabel='K', ylabel='Accuracy')
ax.set(xticks=np.arange(0, num_ks+1,5), yticks=np.arange(0.5,1.0,0.05))
ax.legend()
plt.show()
Output:running KNN with l2 distance metric processing… k= 5 processing… k= 10 processing… k= 15 processing… k= 20 processing… k= 25 processing… k= 30 processing… k= 35 processing… k= 40 processing… k= 45 processing… k= 50
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.